Introduction
Revision hip replacement is a surgical procedure to replace or repair a previously implanted hip prosthesis. It is typically required when the original hip replacement fails due to wear, infection, or other complications. This blog post will cover the reasons for revision hip replacement, the procedure, and the recovery process.
What is Revision Hip Replacement?
Revision hip replacement involves removing the old hip prosthesis and replacing it with a new one. This surgery is more complex than the initial hip replacement due to the altered anatomy and possible bone loss.

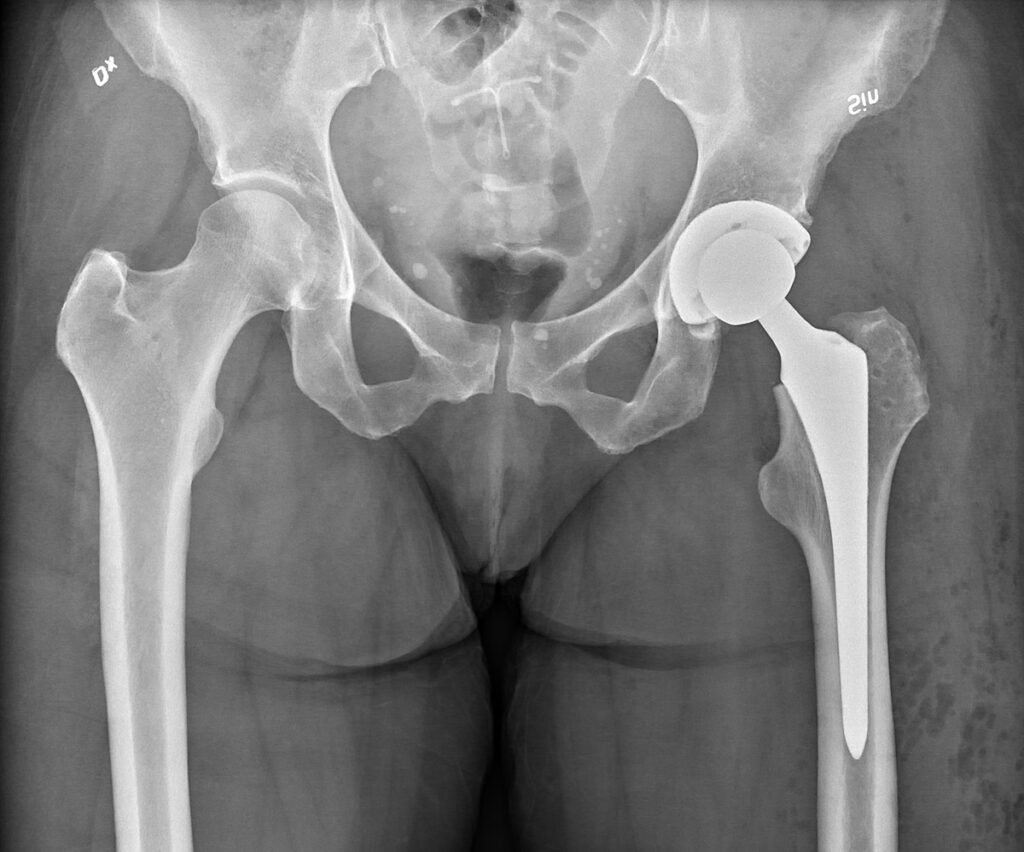
Why is Revision Hip Replacement Needed?
Several factors can lead to the need for a revision hip replacement, including:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the components of the hip replacement can wear out.
- Infection: An infection in the hip joint can necessitate revision surgery.
- Implant Loosening: The prosthesis may become loose or unstable.
- Fractures: Bone fractures around the implant can require revision surgery.
- Dislocation: Recurrent dislocations may indicate a problem with the implant.
The Revision Hip Replacement Procedure
- Pre-Surgery Evaluation: This includes detailed imaging tests, blood work, and discussions about anesthesia and potential risks.
- Surgical Steps:
- Removing the Old Prosthesis: The surgeon carefully removes the existing implant.
- Preparing the Bone: Damaged bone and tissue are cleaned, and any necessary bone grafts are performed.
- Inserting the New Prosthesis: The new hip components are placed and secured.
- Post-Surgery Care: Focuses on pain management, preventing infection, and starting physical therapy.


Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from revision hip replacement can be longer and more involved than the initial surgery. A typical recovery timeline includes:
- Week 1-2: Managing pain, controlling swelling, and beginning gentle exercises.
- Week 3-6: Gradual increase in physical therapy exercises, improving mobility, and reducing the use of assistive devices.
- Week 7 and Beyond: Continued strengthening exercises and slowly resuming normal activities.
Challenges and Considerations
- Complexity: Revision surgeries are more complex due to scar tissue, bone loss, and potential complications.
- Risk of Complications: Higher risk of infection, blood clots, and implant failure compared to initial replacement.
- Extended Recovery: Patients may need more time and effort to regain full function.


Tips for a Successful Recovery
- Adhere to Medical Advice: Follow all post-operative instructions and attend regular follow-up appointments.
- Engage in Physical Therapy: Consistent therapy is crucial for regaining strength and mobility.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet and appropriate exercises can aid in recovery.
- Monitor for Complications: Be vigilant for signs of infection or other issues and contact your healthcare provider if needed.
Conclusion :-
Revision hip replacement is a complex but often necessary procedure to address issues with a previous hip replacement. With proper medical care, thorough rehabilitation, and a positive outlook, patients can achieve significant improvements in function and quality of life. If you think you might need a revision hip replacement, consult with an orthopedic specialist to discuss your options and create a tailored treatment plan.


